Common Health Insurance Terms
A Guide to Health Insurance Terms

The language of health insurance can be hard to understand. Here, you’ll find the most common health insurance terms.
We think you’ll agree that a little knowledge will help you make smart decisions that will benefit you and your family, today and for years to come.
And now, some basic terms:
Accidental dental emergency treatment – Dental treatment in the dental department of a hospital following an accident
Coverage area – The geographical territory where you are covered by your insurance.
Community rated provider – A risk rating method in which an insurer group all of their members together. The premiums of the group are equally raised based on the groups claim ratio in the previous year + inflation. Your renewal insurance premium will be a fixed percentage and will not be higher or lower than any other member, regardless of how much or little you used the insurance in the previous year. Unless the provider offers a no-claims discount.
Day-patient – Being admitted to a hospital but not requiring an overnight stay
Deductibles & Co-Pays
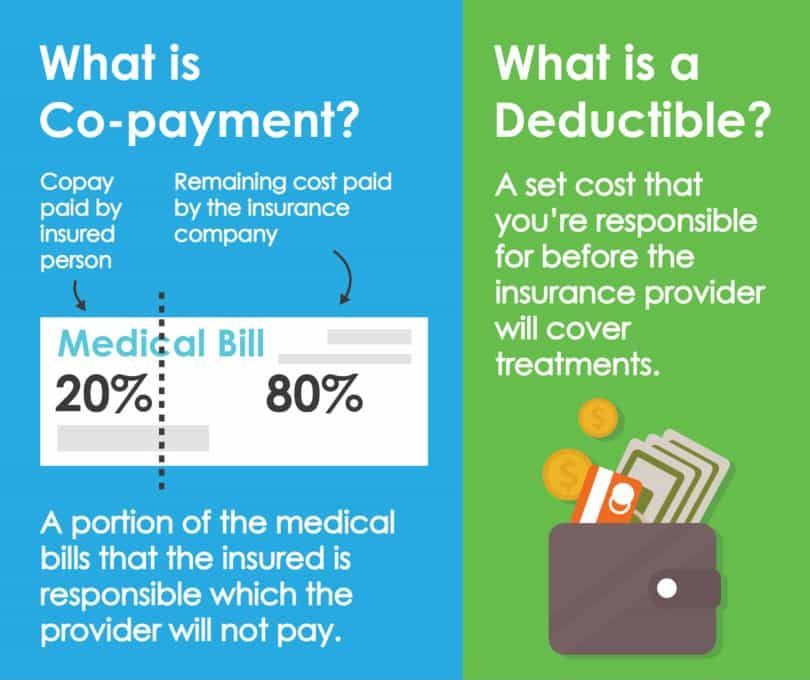
Co-payment – A portion of the medical bills that the insured is responsible which the provider will not pay.
For example, a 25% co-pay means that you are responsible for 25% of the cost of treatment. This may be taken to reduce the initial premium.
Deductible/Excess – A set cost that you’re responsible for before the insurance provider will cover treatments.
For example, a $50/visit excess means that you pay $50 and then the insurance will cover anything after that. This can be per visit, or per year and may be taken to reduce the initial premium.
Direct billing network – The hospitals and clinics an insurer works with that offer cashless system for claims. The insurer will pay the hospital or clinic directly.
Effective date – The date that your insurance policy starts to take effect.
Experience rated provider – The provider evaluates the risk of the insured on an individual basis. They look at how much or little you’ve used your insurance in the previous year.
Emergency evacuation – emergency medical transportation costs if treatment is not available locally. This is only available in a life-threatening situation.
Guarantee of payment – The insurer will issue a guarantee of payment to a hospital which guarantees the payment to the hospital. If the hospital accepts it, then direct billing will apply and you don’t have to pay and claim.
Inpatient / Hospitalization – Being admitted in a hospital to a bed. In most cases, you have to stay overnight
Insurer – The insurance company that provides the insurance cover for your plan.
Insured person – The person that is eligible to get insurance coverage.
Medical repatriation – Being returned to your country of residence or your home country following an emergency medical evacuation.
Newborn free cover – Your newborn will be added at no cost to your insurance policy until the next renewal as long as you sing up for insurance a specific of time before your baby DOB.
Get a Direct Comparison of Insurance Providers
Insurance Simplified
Outpatient – Treatment for injuries, illnesses or medical conditions that do not require hospitalization, in which you go to see a doctor and go home on the same day
Outpatient surgery – This benefit covers you for minor surgical operations that don’t require hospitalization. It’s usually included as an inpatient benefit.
Pre-existing medical conditions – Any disease, illness or injury for which you have received treatments, advice or medication, or experienced symptoms before getting your insurance policy.
Pre-hospitalization – Costs and fees leading up to hospitalization such as consultations, tests, and exams. This is considered an inpatient benefit and usually provides coverage for 30-days prior to hospitalization.
Pre-authorization – An insurance provider may require to be notified to approve treatments, such as planned non-emergency surgeries.
Post-hospitalization – Follow-up treatment that’s required following a hospitalization such as follow-up consultations, exams, tests, and prescribed medicines.
Renewal date – The date when your policy starts again. This is when you can, if allowed, make any changes to your plan.
Repatriation of mortal remains – This benefit pays the cost of sending a deceased person’s body back to their home country. The family can choose to repatriate the body or local cremation. The cost varies depending on how the body is handled and location of repatriation.
Room & board – The type and cost of your room & food. There are private rooms and semi-private rooms.
Routine / Preventive health check – A preventative health check that someone might take when no symptoms are present that’s used as a way for early detection of medical conditions. This might be an annual physical exam or screening.
Underwriting – How the insurance provider evaluates the risk of each person.
Full Medical Underwriting – a comprehensive health declaration related to your medical history.
Moratorium – a basic & short medical declaration.
Waiting period – A period of time you have to wait before a benefit becomes eligible for being paid.
Hopefully, this has shed some light on health insurance to prevent you from common misconceptions and save you money on your premiums.
If that’s too much and you don’t know where to start you can fill out the application form for a no-obligation consultation.


