Cost of Health Insurance in Vietnam
Helping you Navigate the Cost of Health Insurance in Vietnam

There are hundreds of plans available with prices ranging from $100-$10,000+ per year. So why is there such a large gap in the cost of health insurance in Vietnam? That’s what we’ll be looking at today:
Key factors in determining the cost of health insurance
Average cost of health insurance in Vietnam by age & type of policy
First, what is a premium? For those unfamiliar with insurance terms, this may be a new term. This is your cost of health insurance. It’s a precise calculation which takes into account many factors such as age and benefits.
Let’s take a look at some of the most important determining factors on your premium:
1. Age
Unlike a fine wine, your insurance premium does not get better with age. As you age, the higher the likelihood you’ll experience medical conditions which are more severe, frequent and costly. On average, older people are a higher risk for the insurers and thus require higher average premiums. Conversely, younger people are lower risks and their average premiums are lower.
Most providers put people in different age brackets, usually in 5-year increments, with everyone in that age bracket getting charged the same premium. For example:
25-29
30-34
35-39
Not only do you go up in age bracket, but you also increase your premium at an accelerated rate. Here are some sample premiums by age:
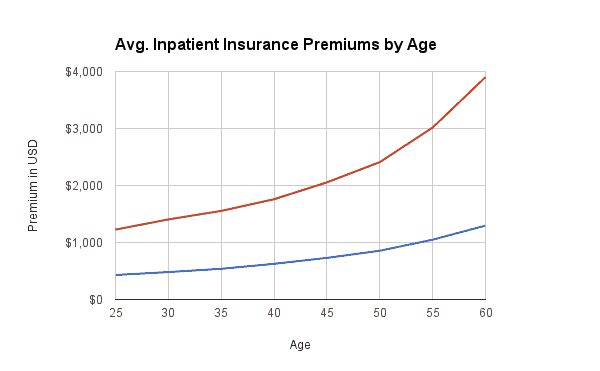
Red = International providers Blue = Vietnamese providers
The above stats are based on a range of plans from different Vietnamese and International insurance providers.
It’s important to note that some providers restrict the age for accepting new applicants, usually at age 60 or 65. There are still options if you’re 65+, just fewer and more expensive.
The takeaway: expect your premium to increase as you age.
2. Coverage Area
Where you’re covered at and the cost of healthcare in those countries will have an impact on the cost of health insurance in Vietnam. You may travel a lot and require a worldwide plan. You may only need coverage in SE Asia. In general, there are four main coverage areas:
Residence country only – such as Vietnam only or Thailand only.
SE Asia – Coverage is restricted to Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines and Indonesia. Many providers who offer SE Asia plans exclude Singapore from coverage to help keep premiums down as healthcare in Singapore is higher.
Worldwide excluding the USA and other countries – Providers often have policies which restrict coverage to USA. Sometimes coverage is restricted to Canada or all of North America. Some providers will go further and restrict coverage to other high-cost places such as Singapore, Hong Kong, places in Europe.
Worldwide – A truly worldwide plan covers you worldwide, no matter where you are in the world. If your benefits are comprehensive, then you’ll have to pay a heft for this option.
Often times you may have emergency coverage for outside of your regular coverage area. This will at least provide you some coverage in the event you’re travelling somewhere outside your regular zone.
3. Benefits
Coupled with age, the benefits selected have a major effect on the cost of health insurance in Vietnam. A standard plan includes inpatient (hospitalisation) and it usually includes emergency medical evacuation and/or repatriation. There are also a number of other benefits that can be added on to your plan. The more benefits you have, the higher the premium.
The most notable addition is the outpatient benefit, which covers you for everyday treatments at a doctor’s office or clinic. Think of minor injuries, illnesses or medical conditions where you go to a clinic and go back home afterward. Premiums often jump 30%-100%+ when outpatient treatment is added. This is because it’s the most commonly used benefit and when people have it, they use it.
Other benefits which can drive your premium up include:
Dental
Wellness/Preventative
Vision
USA Coverage
Personal Accident insurance
4. Benefit Levels & Limitations
Not only are the actual benefits important, so too are the levels and limitations. The higher the benefits and less restricted your plan is, the higher your premium will be. A plan with a $50,000 maximum is more affordable than a plan with a $1,000,000 max. While it’s unlikely that you’ll need a $1,000,000 in a given year, plans that have a higher annual maximum will be more comprehensive across other benefits.
So some interesting things here:
1. Plan 1 is the cheapest even though it’s a worldwide policy. While plan 2 & 3 restrict the coverage area and cost more. The risk to the insurer for plan 1 is much lower than plan 2 or 3, as the maximum payable benefits are lower (There are also other factors going into this premium difference)
2. The cost % increase to add outpatient for Plan 1 is much lower than Plan 2 or Plan 3. This is because it’s a commonly used benefit and it’s limited to $120/visit, so the insurer takes on less risk to offer the benefit. A $500 outpatient visit will cost provider 1 $120, while it will cost provider 2 & 3 $500 respectively.
3. Both Plan 2 & Plan 3 would be comprehensive plans for their benefits, yet there’s a big premium difference between them. When you expand the regular coverage area & annual maximum, you see a much higher premium.
Other key benefits which you might see limits on which would affect your premium are:
Room & Board
Pre & Post hospitalisation
Physiotherapy, Chiropractor, Acupuncture
Wellness/ Preventative checks
Dental
Maternity
5. Medical History/Pre-Existing Conditions
To get insured for a pre-existing condition from the onset of the policy is not impossible. However, expect to pay an additional premium to do so. While there’s no guarantee that you can get insured for an existing condition, an insurer will consider applying a medical loading to cover your condition. In that situation you can either have your pre-existing condition:
Covered with no loading
Covered with a premium loading
Excluded from coverage
This is done on a case-by-case basis and it depends on the condition and the risk to the insurer for future treatments. For example, someone with asthma might be offered coverage under the condition they take a 15% premium loading to have claims related to asthma covered.
6. Elective Treatment
Many expats living in SE Asia would elect to have non-emergency treatment somewhere other than their residence country. This is elective treatment. Some providers allow you the option to have the coverage anywhere in your coverage area. Other providers may deny or restrict the maximum benefits payable if you chose to do this.
If your plan allows freedom of treatment then you should expect your premium is more. After all, the average cost of treatment at a top hospital in Bangkok is more than at a top hospital in Vietnam.
As a rule of thumb, international providers allow you to receive treatment anywhere instead of your coverage area that you choose. Some Vietnamese providers allow elective coverage, some don’t and some require you to submit quotations to them for pre-authorization before this could be done.
7. Inflation
When your policy comes time to renew, your premium may increase even though you haven’t claimed or changed age brackets. If that’s the case, then it’s likely you premium was increased due to economic and medical inflation. As the cost of healthcare and treatments rise, so too will your premium.
8. Occupation
If your job exposes you to higher rates of risk for injury, then you may have an occupational hazard loading. This is often seen with oil and gas, factory, engineers, or in construction.
If a job is too risky an exclusion may apply which excludes coverage while you’re at work. If that’s the case you’d want to make sure your employer-provided worker’s compensation insurance to cover any medical expenses that occurred while on the job.
Get a Direct Comparison of Insurance Providers
Insurance Simplified
9. Deductible, Excesses & Co-Pays
You may choose to take annual deductible, a per visit excess or a co-pay. All of these will affect your premium, either by taking one or not taking one.
A deductible is an annual deductible is a fixed amount that you must pay before the insurance will start to cover you for your eligible expenses. For example, you might have an annual $250 deductible per person. This means that you’re responsible for the first $250 of eligible expenses, then the insurance will cover all other eligible expenses after that. Typical deductibles range from $250/year all the way up to $5,000/year+. Depending on the provider, the deductible may apply to all of your expenses or only your inpatient expenses.
An excess is a synonym for a deductible. Excess is commonly used term in the UK.
A co-pay: you may also choose to take a co-pay, which means you agree to share a fixed percentage of the eligible costs with the insurer. Typically this is between 10-20%. If you took a 20% co-pay and had a $1,000 bill, then you’d have to pay $200 and the insurer would pay $800. This can get expensive for high-ticket treatments. The same 20% co-pay would set you back $2,000 on at $10,000 hospital bill.
10. Payment Instalments
If you’re paying monthly, Quarterly or Semi-annually, you can expect to incur an additional surcharge for doing so.
Monthly payments: 5-10% more on your annual premium
Quarterly payments: 5%-7.5% more on your annual premium
Semi-annual payments: 4%-6% on your annual premium
11. Family/ Child Discounts
You may be eligible for a family discount if you’re insuring 3+ members simultaneously. Other providers may offer discounted rates for having 2+ children, sometimes even offering free coverage on your 2nd, 3rd, and 4th child.
So How Much Does It Cost?
The million-dollar question that everyone wants to know. While everyone’s insurance needs and budget are unique to themselves, we’ve broken down the average premiums by age from a range of different Vietnamese and International providers. They show options for:
Inpatient plans
Inpatient & Outpatient
Inpatient, Outpatient & Dental
Cost of Health Insurance in Vietnam
TABLE
Insurance premiums for International providers
TABLE
While everyone’s insurance needs and budget are unique, hopefully, this has shed some light on the cost of health insurance in Vietnam and the key factors that determine the price. Remember, there’s a plan out there for you, regardless of your budget. You can save money on your health insurance costs if you do your research and shop around. If that’s too much and you don’t know where to start you can contact us today to get started.


